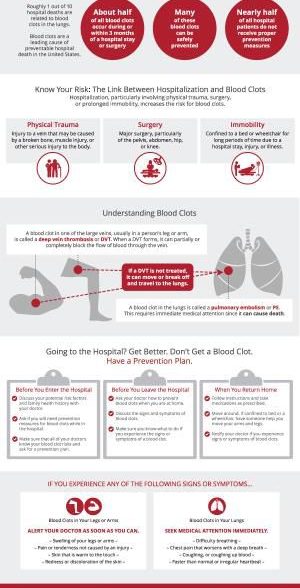
(StatePoint) Each year, dangerous blood clots affect about 900,000 people nationwide, and about half of all blood clots occur during a hospital stay or within three months of a hospital stay or surgery.
Hospitalization is a major risk factor for blood clots. While most blood clots can be prevented, nearly half of hospital patients do not receive proper prevention measures.
Click Here to Enlarge Infographic.
Dangerous blood clots occur most often in the leg or arm. A blood clot in your leg can move or break apart and travel to your lungs, which can be deadly. The symptoms of a blood clot in your leg or arm include swelling, pain or tenderness, and skin that may be warm to the touch or discolored. The symptoms of a blood clot in your lung include difficulty breathing, chest pain that worsens with a deep breath, and coughing up blood. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
If you or someone you know is going to the hospital, make a prevention plan. More information about blood clots and how they can be prevented is available at stoptheclot.org/spreadtheword.
Get better. Don’t get a blood clot.